 reader comments
reader comments
18 with 18 posters participating
If you use Alexa, Echo, or any other Amazon device, you have only 10 days to opt out of an experiment that leaves your personal privacy and security hanging in the balance.
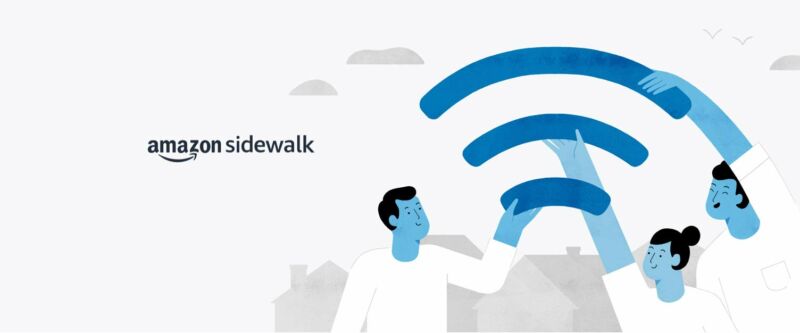
On June 8, the merchant, Web host, and entertainment behemoth will automatically enroll the devices in Amazon Sidewalk. The new wireless mesh service will share a small slice of your Internet bandwidth with nearby neighbors who don’t have connectivity and help you to their bandwidth when you don’t have a connection.
By default, Amazon devices including Alexa, Echo, Ring, security cams, outdoor lights, motion sensors, and Tile trackers will enroll in the system. And since only a tiny fraction of people take the time to change default settings, that means millions of people will be co-opted into the program whether they know anything about it or not.
Amazon has published a white paper detailing the technical underpinnings and service terms that it says will protect the privacy and security of this bold undertaking. To be fair, the paper is fairly comprehensive, and so far no one has pointed out specific flaws that undermine the encryption or other safeguards being put in place. But there are enough theoretical risks to give users pause.
Wireless technologies like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth have a history of being insecure. Remember WEP, the encryption scheme that protected Wi-Fi traffic from being monitored by nearby parties? It was widely used for four years before researchers exposed flaws that made decrypting data relatively easy for attackers. WPA, the technology that replaced WEP, is much more robust, but it also has a checkered history.
share of similar vulnerabilities over the years, too, either in the Bluetooth standard or in the way it’s implemented in various products.
If industry-standard wireless technologies have such a poor track record, why are we to believe a proprietary wireless scheme will have one that’s any better?
The omnipotent juggernaut
Next, consider the wealth of intimate details Amazon devices are privy to. They see who knocks on our doors, and in some homes they peer into our living rooms. They hear the conversations we’re having with friends and family. They control locks and other security systems in our home.
Extending the reach of all this encrypted data to the sidewalk and living rooms of neighbors requires a level of confidence that’s not warranted for a technology that’s never seen widespread testing.
Last, let’s not forget who’s providing this new way for everyone to share and share alike. As independent privacy researcher Ashkan Soltani puts it: “In addition to capturing everyone’s shopping habits (from amazon.com) and their internet activity (as AWS is one of the most dominant web hosting services)… now they are also effectively becoming a global ISP with a flick of a switch, all without even having to lay a single foot of fiber.”
Amazon’s decision to make Sidewalk an opt-out service rather than an opt-in one is also telling. The company knows the only chance of the service gaining critical mass is to turn it on by default, so that’s what it’s doing. Fortunately, turning Sidewalk off is relatively painless. It involves:
- Opening the Alexa app
- Opening More and selecting Settings
- Selecting Account Settings
- Selecting Amazon Sidewalk
- Turning Amazon Sidewalk Off
No doubt, the benefits of Sidewalk for some people will outweigh the risks. But for the many, if not the vast majority of users, there’s little upside and plenty of downside. Amazon representatives didn’t respond to a request for comment.