reader comments
26
The FBI spent much of Tuesday locked in an online tug-of-war with one of the Internet’s most aggressive ransomware groups after taking control of infrastructure the group has used to generate more than $300 million in illicit payments to date.
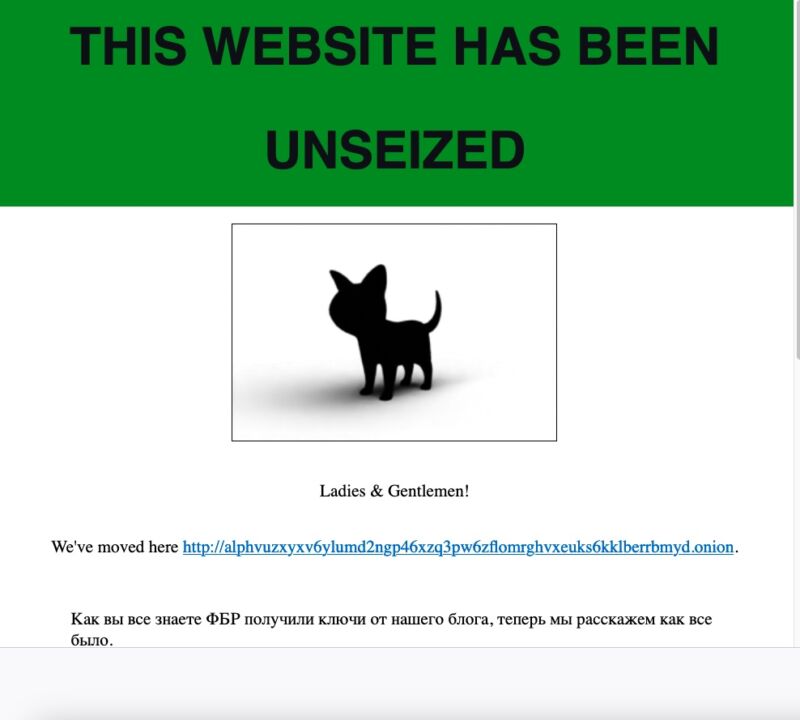
Early Tuesday morning, the dark-web site belonging to AlphV, a ransomware group that also goes by the name BlackCat, suddenly started displaying a banner that said it had been seized by the FBI as part of a coordinated law enforcement action. Gone was all the content AlphV had posted to the site previously.

Around the same time, the Justice Department said it had disrupted AlphV’s operations by releasing a software tool that would allow roughly 500 AlphV victims to restore their systems and data. In all, Justice Department officials said, AlphV had extorted roughly $300 million from 1,000 victims.
An affidavit unsealed in a Florida federal court, meanwhile, revealed that the disruption involved FBI agents obtaining 946 private keys used to host victim communication sites. The legal document said the keys were obtained with the help of a confidential human source who had “responded to an advertisement posted to a publicly accessible online forum soliciting applicants for Blackcat affiliate positions.”
“In disrupting the BlackCat ransomware group, the Justice Department has once again hacked the hackers,” Deputy Attorney General Lisa O. Monaco said in Tuesday’s announcement. “With a decryption tool provided by the FBI to hundreds of ransomware victims worldwide, businesses and schools were able to reopen, and health care and emergency services were able to come back online. We will continue to prioritize disruptions and place victims at the center of our strategy to dismantle the ecosystem fueling cybercrime.”
tug of Tor,” a reference to Tor, the network of servers that allows people to browse and publish websites anonymously. Like most ransomware groups, AlphV hosts its sites over Tor. Not only does this arrangement prevent law enforcement investigators from identifying group members, it also hampers investigators from obtaining court orders compelling the web host to turn over control of the site.
The only way to control a Tor address is with possession of a dedicated private encryption key. Once the FBI obtained it, investigators were able to publish Tuesday’s seizure notice to it. Since AlphV also maintained possession of the key, group members were similarly free to post their own content. Since Tor makes it impossible to change the private key corresponding to an address, neither side has been able to lock the other out.
With each side essentially deadlocked, AlphV has resorted to removing some of the restrictions it previously placed on affiliates. Under the common ransomware-as-a-service model, affiliates are the ones who actually hack victims. When successful, the affiliates use the AlphV ransomware and infrastructure to encrypt data and then negotiate and facilitate a payment by bitcoin or another cryptocurrency.
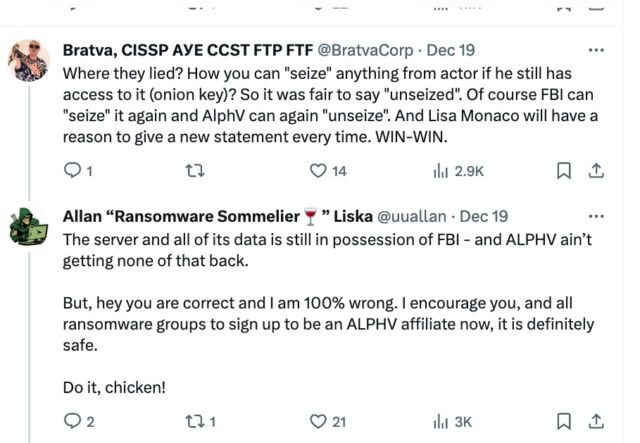
“But, hey you are correct and I am 100% wrong. I encourage you, and all ransomware groups to sign up to be an ALPHV affiliate now, it is definitely safe. Do it, Chicken!”