reader comments
64 with
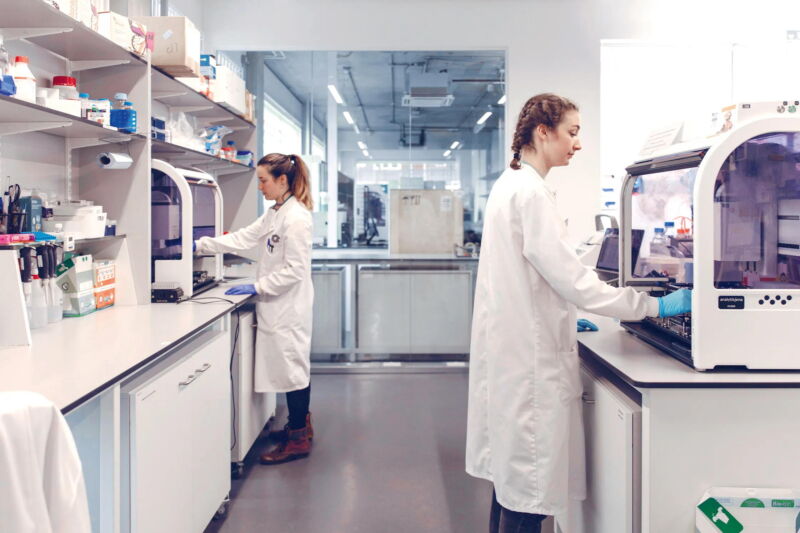
At an old biscuit factory in South London, giant mixers and industrial ovens have been replaced by robotic arms, incubators, and DNA sequencing machines. James Field and his company LabGenius aren’t making sweet treats; they’re cooking up a revolutionary, AI-powered approach to engineering new medical antibodies.
In nature, antibodies are the body’s response to disease and serve as the immune system’s front-line troops. They’re strands of protein that are specially shaped to stick to foreign invaders so that they can be flushed from the system. Since the 1980s, pharmaceutical companies have been making synthetic antibodies to treat diseases like cancer, and to reduce the chance of transplanted organs being rejected.

But designing these antibodies is a slow process for humans—protein designers must wade through the millions of potential combinations of amino acids to find the ones that will fold together in exactly the right way, and then test them all experimentally, tweaking some variables to improve some characteristics of the treatment while hoping that doesn’t make it worse in other ways. “If you want to create a new therapeutic antibody, somewhere in this infinite space of potential molecules sits the molecule you want to find,” says Field, the founder and CEO of LabGenius.
He started the company in 2012 when, while studying for a PhD in synthetic biology at Imperial College London, he saw the costs of DNA sequencing, computation, and robotics all coming down. LabGenius makes use of all three to largely automate the antibody discovery process. At the lab in Bermondsey, a machine learning algorithm designs antibodies to target specific diseases, and then automated robotic systems build and grow them in the lab, run tests, and feed the data back into the algorithm, all with limited human supervision. There are rooms for culturing diseased cells, growing antibodies, and sequencing their DNA: Technicians in lab coats prepare samples and tap away at computers as machines whir in the background.
wired.com.