 reader comments
reader comments
48 with 33 posters participating, including story author
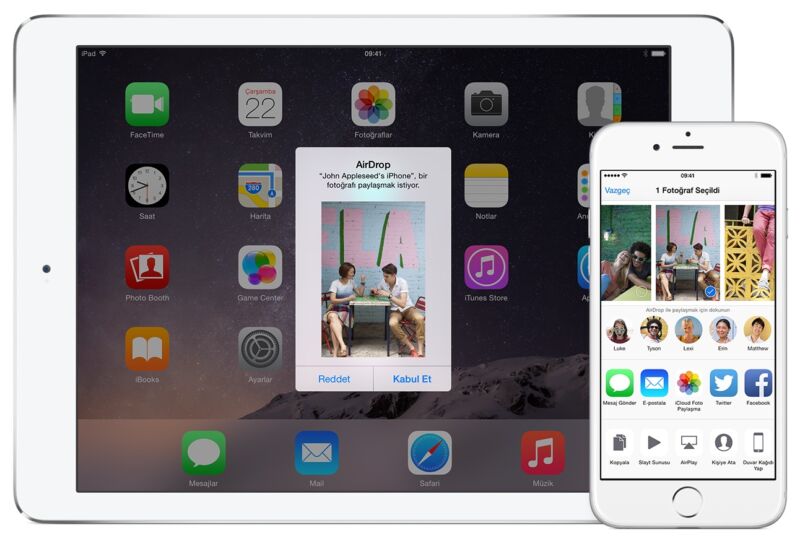
AirDrop, the feature that allows Mac and iPhone users to wirelessly transfer files between devices, is leaking user emails and phone numbers, and there’s not much anyone can do to stop it other than to turn it off, researchers said.
AirDrop uses Wi-Fi and Bluetooth Low Energy to establish direct connections with nearby devices so they can beam pictures, documents, and other things from one iOS or macOS device to another. One mode allows only contacts to connect, a second allows anyone to connect, and the last allows no connections at all.
A matter of milliseconds
To determine if the device of a would-be sender should connect with other nearby devices, AirDrop broadcasts Bluetooth advertisements that contain a partial cryptographic hash of the sender’s phone number and email address. If any of the truncated hashes matches any phone number or email address in the address book of the receiving device or the device is set to receive from everyone, the two devices will engage in a mutual authentication handshake over Wi-Fi. During the handshake, the devices exchange the full SHA-256 hashes of the owners’ phone numbers and email addresses.
Hashes, of course, can’t be converted back into the cleartext that generated them, but depending on the amount of entropy or randomness in the cleartext, they are often possible to figure out. Hackers do this by performing a “brute-force attack,” which throws huge numbers of guesses and waits for the one that generates the sought-after hash. The less the entropy in the cleartext, the easier it is to guess or crack, since there are fewer possible candidates for an attacker to try.
The amount of entropy in a phone number is so minimal that this cracking process is trivial since it takes milliseconds to look up a hash in a precomputed database containing results for all possible phone numbers in the world. While many email addresses have more entropy, they too can be cracked using the billions of email addresses that have appeared in database breaches over the past 20 years.
paper presented in August at the USENIX Security Symposium, Weinert and researchers from TU Darmstadt’s SEEMOO lab devised two ways to exploit the vulnerabilities.
The easiest and most powerful method is for an attacker to simply monitor the discovery requests that other nearby devices send. Since the sender device always discloses its own hashed phone number and email address every time it scans for available AirDrop receivers, the attacker need only wait for nearby Macs to open the share menu or nearby iOS devices to open the share sheet. The attacker need not have the phone number, email address, or any other prior knowledge of the target.
A second method works largely in reverse. An attacker can open a share menu or share sheet and see if any nearby devices respond with their own hashed details. This technique isn’t as powerful as the first one because it works only if the attacker’s phone number or email address is already in the receiver’s address book.
Still, the attack could be useful when the attacker is someone whose phone number or email address is well known to many people. A manager, for instance, could use it to get the phone number or email address of any employees who have the manager’s contact information stored in their address books.
In an email, Weinert wrote:
What we call “sender leakage” (i.e., somebody who intends to share a file leaks their hashed contact identifiers) could be exploited by planting “bugs” (small Wi-Fi enabled devices) in public hot spots or other places of interest.
Say, you plant such a bug in a conference room or an event where politicians, celebrities, or other “VIPs” come together (e.g., Oscar Awards). As soon as one of them opens the sharing pane on an Apple device, you can get hold of at least their private mobile phone number.
From a reporter perspective a scenario for what we call “receiver leakage”: Say you have been in email contact with a celebrity to cover a story. In case the celebrity has therefore stored your email address, you can easily get hold of their private mobile phone number when being in proximity (e.g., during an interview). In this case, the celebrity [does] not even have to open the sharing pane or otherwise touch their device!
Two years of silence from Apple
The researchers say they privately notified Apple of their findings in May 2019. A year and a half later, they presented Apple with “PrivateDrop,” a reworked AirDrop they developed that uses private set intersection, a cryptographic technique that allows two parties to perform contact discovery process without disclosing vulnerable hashes. The implementation of PrivateDrop is publicly available on GitHub.
post summarizing their work.
As of this week, Apple has yet to indicate if it has plans to adopt PrivateDrop or employ some other way to fix the leakage. Apple representatives didn’t respond to an email seeking comment for this post.
What this means is that every time someone opens a sharing panel in either macOS or iOS, they’re leaking hashes that, at a minimum, disclose their phone numbers and likely their email addresses, too. And in some cases, just having AirDrop enabled at all may be enough to leak these details.
Weinert said that, for now, the only way to prevent the leakage is to set AirDrop discovery to “no one” in the system settings menu and to also refrain from opening the sharing pane. When using AirDrop at home or other familiar settings, this advice may be overkill. It may make more sense when using a computer at a conference or other public venue.