Shira Fishbach, a newly graduated physician, was sitting in an orientation session for her first year of medical residency when her phone started blowing up. It was June 24, 2022, and the US Supreme Court had just handed down its decision in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization, nullifying the national right to abortion and turning control back to state governments.
Fishbach was in Michigan, where an abortion ban enacted in 1931 instantly came into effect. That law made administering an abortion a felony punishable by four years in prison, with no exceptions for rape or incest. It was a chilling moment: Her residency is in obstetrics and gynecology, and she viewed mastering abortion procedures as essential to her training.
“I suspected during my application cycle that this could happen, and to receive confirmation of it was devastating,” she recalls. “But I had strategically applied where I thought that, even if I didn’t receive the full spectrum, I would at least have the support and the resources to get myself to an institution that would train me.”
Her mind whirled through the possibilities. Would her program help its residents go to an access-protecting state? Could she broker an agreement to go somewhere on her own, arranging weeks of extra housing and obtaining a local medical license and insurance? Would she still earn her salary if she left her program—and how would she fund her life if she did not?
In the end, she didn’t need to leave. That November, Michigan voters approved an amendment to the state constitution that made the 1931 law unenforceable, and this April, Governor Gretchen Whitmer repealed the ban. Fishbach didn’t have to abandon the state to learn the full range of ob-gyn care. In fact, her program at the University of Michigan, where she’s now a second-year resident, pivoted to making room for red-state trainees.
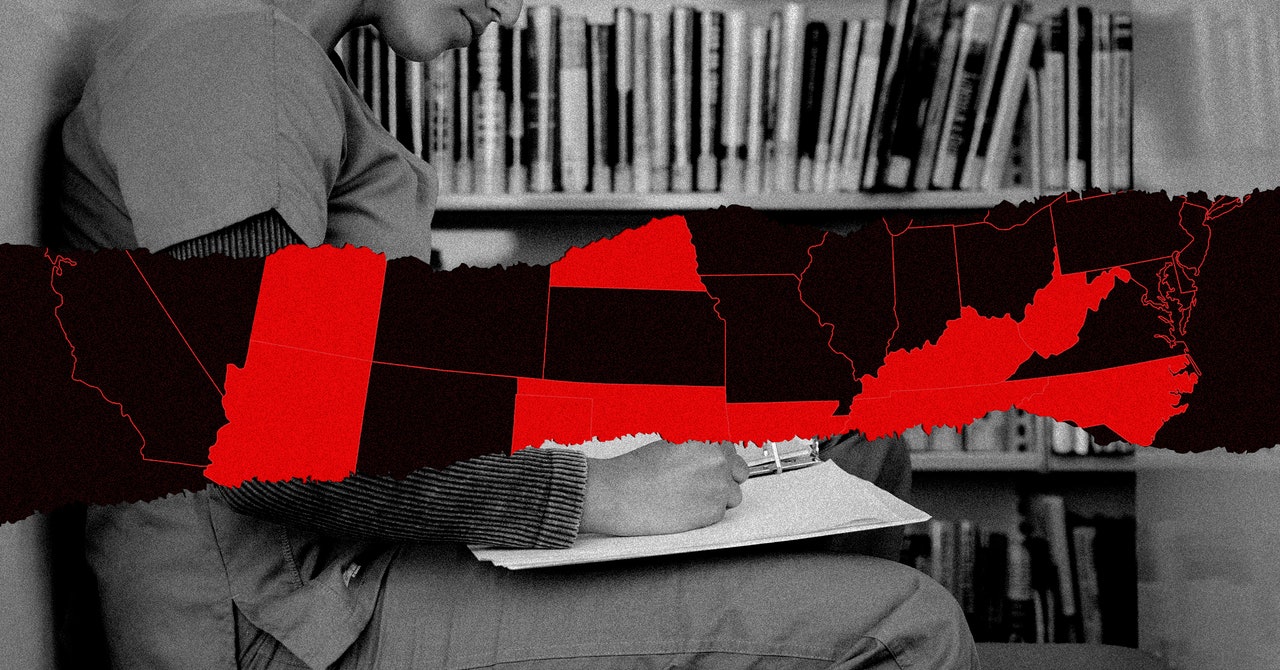
But the dizzying reassessment she underwent a year ago provides a glimpse of the challenges that face thousands of new and potential doctors. Almost 45 percent of the 286 accredited ob-gyn programs in the US now operate under revived or new abortion bans, meaning that more than 2,000 residents per year—trainee doctors who have committed to the specialty—may not receive the required training to be licensed. Among students and residents, simmering anger over bans is growing. Long-time faculty fear the result will be a permanent reshaping of American medicine, driving new doctors from red states to escape limitations and legal threats, or to protect their own reproductive options. That would reduce the number of physicians available, not just to provide abortions, but to conduct genetic screenings, care for miscarriages, deliver babies, and handle unpredictable pregnancy risks.
“I worry that we’re going to see an increase in maternal morbidity, differentially, depending on where you live,” says Kate Shaw, a physician and associate chair of ob-gyn education at Stanford Medicine. “And that’s just going to further enhance disparities that already exist.”
Those effects are not yet visible. The pipeline that ushers medical graduates through physician training is about a decade long: four years of school plus three to seven years of residency, sometimes with a two-year, sub-specialty fellowship afterward. Thus actions taken in response to the Dobbs decision—people eschewing red-state schools or choosing to settle in blue states long-term—might take a while to be noticeable.